Politics & Government
Arkansas Opens EV Charging Station Rebate Program Early To Meet High Demand
The rebates can cover up to 90% of the costs of eligible public "Level 2" charging stations, which can charge vehicles in eight hours.
- October 13, 2022
Arkansas’ environmental regulators this week made a new round of rebates available early for community electric vehicle charging stations thanks to surging interest in expanding the state’s EV infrastructure.
Find out what's happening in Across Arkansasfor free with the latest updates from Patch.
The rebates can cover up to 90% of the costs of eligible public “Level 2” charging stations, which can charge vehicles in eight hours or less.
The rebate program is one of several approaches the state is using to build out its EV charging network, which has lagged behind other states.
Find out what's happening in Across Arkansasfor free with the latest updates from Patch.
Arkansas Department of Energy and Environment Secretary Becky Keough said there’s an urgency to deploy charging stations to communities, and she expects demand to continue to grow with the rising popularity and affordability of electric vehicles.
The current round of rebates, nearly $230,000, wasn’t planned to become available until 2023, but Keogh said her agency received greater-than-expected interest.
“I couldn’t be any more excited about broadening EV infrastructure across our state,” she said. “Due to the overwhelming amount of interest, we made the decision to make the last round of funding available now for the public. I’m encouraging all entities that have installed charging stations after February of this year, to apply for reimbursement. Rebates are awarded on a first-come, first-serve basis.”
Close Embed the Alternative Fueling Station Locator
Embed the station locator using the results you are currently viewing as the default.
HTML
Copy and paste this HTML into your website.
Close
About the Alternative Fueling Station Data
Learn about the station location data collection methods, update schedules, and station details.
Data Collection Methods
The data in the Alternative Fueling Station Locator are gathered and verified through a variety of methods. The National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) obtains information about new stations from trade media, Clean Cities coordinators, the Submit New Station form on the Station Locator website, and through collaborating with infrastructure equipment and fuel providers, original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), and industry groups.
Users submitting updates through the "Submit New Station" or "Report a Change" forms will receive an email confirmation of their submittal. NREL will verify station details before the station is added or updated in the Station Locator. The turnaround time for updates will depend on the completeness of the information provided, as well as the responsiveness of the station or point of contact.
NREL regularly compares its station data with those of other relevant trade organizations and websites. Differences in methodologies, data confirmation, and inclusion criteria may result in slight variations between NREL's database and those maintained by other organizations. NREL also collaborates with alternative fuel industry groups to identify discrepancies in data and develop data sharing processes and best practices. NREL and its data collection subcontractor are currently collaborating with natural gas, electric drive, biodiesel, ethanol, hydrogen, and propane industry groups to ensure best practices are being followed for identifying new stations and confirming station changes in the most-timely manner possible.
Station Update Schedule
Existing stations in the database are contacted at least once a year on an established schedule to verify they are still operational and providing the fuel specified. Based on an established data collection schedule, the database is updated on an ongoing basis. Stations that are no longer operational or no longer provide alternative fuel are removed from the database as they are identified.
Beginning in 2021, public, non-networked electric vehicle (EV) charging stations will be proactively verified every other year, with half of the EV charging stations verified each year. This adjustment is to accommodate the growing number of EV charging stations in the Station Locator. NREL will continue to make updates to any station record if changes are reported.
Mapping and Counting Methods
Each point on the map is counted as one station in the station count. A station appears as one point on the map, regardless of the number of fuel dispensers or electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE) ports at that location. Station addresses are geocoded and mapped using an automatic geocoding application. The geocoding application returns the most accurate location based on the provided address. Station locations may also be provided by external sources (e.g., station operators) and/or verified in a geographic information system (GIS) tool. This information is considered highly accurate, and these coordinates override any information generated using the geocoding application.
Notes about Specific Station Types
- Private Stations
The Station Locator defaults to searching only for public stations. To include private stations in the search, use the Station button on the "Advanced Filters" tab.
Stations with an access listing of "Private - Fleet customers only" may allow other entities to fuel through a business-to-business arrangement. For more information, fleet customers should refer to the information listed in the details section for that station and contact the station directly.
The Station Locator includes information on private fleet fueling stations (e.g., transit bus fueling facilities, other medium- and heavy-duty fueling and charging infrastructure), workplace charging stations, and multi-family housing charging stations. Note that information on these stations is not always published online or in the data download but may be tracked only in the backend Station Locator database. Information tracked only in the backend database may be provided by request to the webmaster listed in the "More Information" section below.
- Planned and Temporarily Unavailable Stations
NREL collects and publishes data on planned station locations, particularly those that are sited and have begun the installation process. In addition, the Station Locator includes stations that are temporarily out of service or offline with plans to open again in the future. To include planned and temporarily unavailable stations in the search results, use the "Advanced Filters" tab.
The Station Locator only includes stations offering biodiesel blends of 20% (B20) and above for a certain period of time during the year. The available blends at each station location are displayed when the station location is selected.
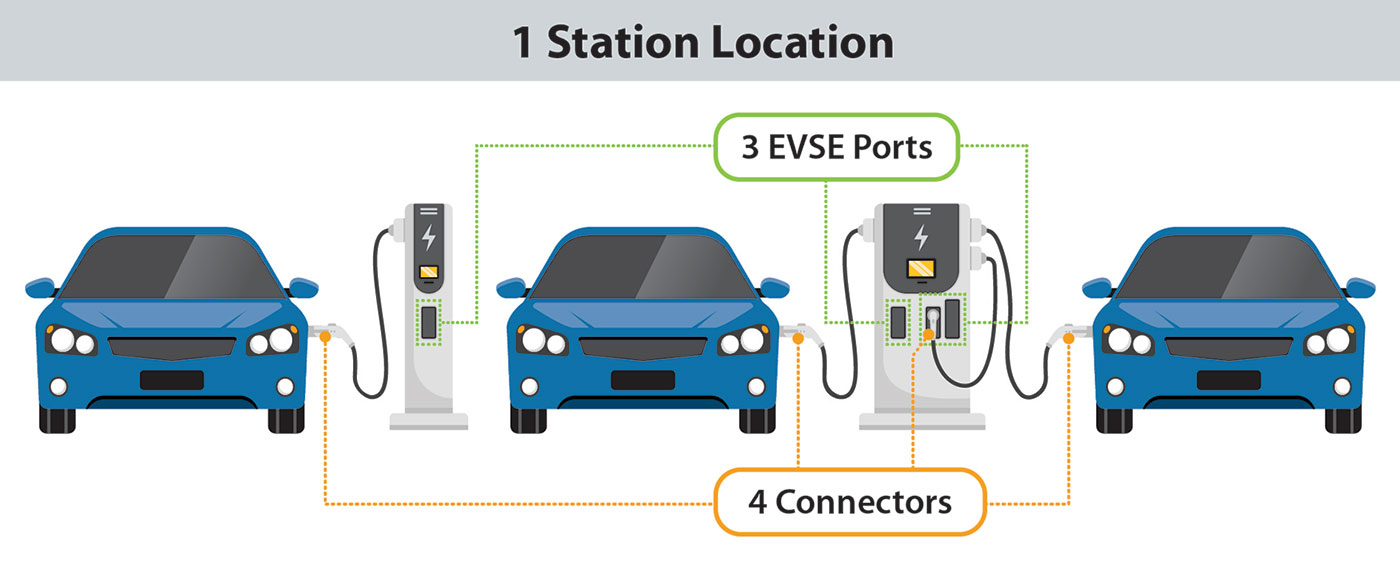
Each point on the map is counted as one station in the station count. The number of EVSE ports and types of connectors available at each station location are displayed in the details page for each station location. Users may search by charger types, connectors, and networks using the Fuel button on the "Advanced Filters" tab.
NREL is in the process of transitioning EV charging station counting logic to align with the hierarchy defined in the Open Charge Point Interface (OCPI) protocol: station location, EVSE port, and connector. With this transition, NREL is updating the number of EVSE ports (formerly called charging outlets) in the Stations Locator, which represents the number of vehicles that can charge simultaneously at a station location. The Station Locator also identifies the available connector types. Both the total number of station locations and EVSE ports appear in the EV charging search results on the "Advanced Filters" tab.
The Station Locator imports Blink, ChargePoint, Electrify America, EVgo, FLO, Greenlots, OpConnect, SemaConnect, and Webasto network station data directly from these networks on a daily basis. Please note there may be variations in the formatting of API stations from other alternative fuels in the Station Locator. Also note, NREL cannot edit station information for the networks listed above. To suggest edits to these stations, please contact the charging network directly with the recommended changes. For network contact information, please contact the webmaster listed in the "More Information" section below.
As the above networks transition to the OCPI protocol, NREL works with each to integrate their OCPI-based API. This transition may result in increases to station counts because of the way that station data are shared under the protocol; one station may be split out into several new stations to represent different physical locations of EV chargers at one address (e.g., opposite sides of one parking lot). While the new stations may share the same street address, they may have different coordinates.
Please Note: Residential EV charging locations and "wall outlets" not designated for vehicle charging are not included in the Station Locator, but workplace charging locations are.
The Station Locator includes stations offering high-level ethanol-gasoline blends (E85). Users may limit their search to E85 stations offering mid-level blends, such as E30, by using the Fuel button on the "Advanced Filters" tab.
Because many public propane stations serve customers other than drivers and fleets, NREL collaborated with propane industry partners to establish and represent the differences. Each public propane station is designated as a "primary" or "secondary" service type, with both types able to fuel propane vehicles. However, locations with a "primary" designation offer vehicle-specific fueling capabilities.
Public locations with the "primary" designation must be staffed during regular business hours and must not require drivers to call ahead in order to fuel. Primary stations must also accept credit cards or fleet cards as a payment type. To be considered "primary," the station must be able to fuel vehicles at a rate of 8-12 gallons per minute or faster, or at a rate similar to filling a gasoline vehicle.
Service designations are available in the details page for each public station. The Station Locator defaults to showing only public "primary" stations. Users may expand their search to include all propane stations by using the "Include stations with limited vehicle fueling" checkbox after choosing propane as a fuel or select this same option in the "Advanced Filters" tab.
Note that several states, including Alabama, Indiana, Kansas, Missouri, and Oklahoma, require or allow in-state propane vehicles to obtain a decal in lieu of paying state fuel taxes at the pump. Out-of-state vehicles may still be subject to taxes at the pump. Determinations about price differential are made assuming that the vehicle has an in-state decal. For more information about state decals and similar laws and regulations, visit the AFDC Laws & Incentives database.
Some compressed and liquefied natural gas stations are not able to fuel larger vehicles due to access limitations, such as a low canopy, insufficient parking adjacent to the pump, or limited space to maneuver. Natural gas station details include vehicle accessibility information, specifically the vehicle classes that can physically access the fueling infrastructure. Please note, this field does not take into account station capacity, throughput, or other considerations. Options include:
- Accommodates passenger vehicles only (Class 1-2).
- Accommodates medium-duty vehicles (Class 3-5).
- Accommodates heavy-duty vehicles (Class 6-8).
- Accommodates all vehicle sizes and classes.
Compressed natural gas stations also list fill type and fill pressure in the details page. These fields are also searchable using the Fuel button on the "Advanced Filters" tab.
Fuel cell electric vehicle drivers have access to hydrogen stations in certain areas of the country. Because this technology is in the early commercialization stages, the status of hydrogen fueling stations may change more frequently than other fuel types. To allow users to monitor station status more closely, hydrogen stations now indicate whether or not they have reduced fueling capacity.
NREL collaborated with industry groups to revisit the definition of public hydrogen stations and refined the Station Locator data to differentiate between stations that are only available to a certain subset of customers (e.g., require an access card, PIN, or training) and those that are considered retail locations (e.g., accept payment at the point of sale). Access designations are available in the details page for each public station. The Station Locator defaults to showing only public retail stations. Users may expand their search to include all public hydrogen stations by selecting the "Include non-retail stations" checkbox.
Download Data
You can download the station data using:
More Information
For more information about the data, contact the webmaster or refer to the list of data fields.
Caution: The AFDC recommends users verify a station is open, available to the public, and has the desired alternative fuel prior to making a trip to that location.
Data Collection Methods
The data in the Alternative Fueling Station Locator are gathered and verified through a variety of methods. National Resources Canada (NRCan) obtains information about new stations from trade media, the Submit New Station form on the Station Locator website, and through collaborating with infrastructure equipment and fuel providers, original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), and industry groups.
Users submitting updates through the "Submit New Station" or "Report a Change" forms will receive an email confirmation of their submittal. NRCan will verify station details before the station is added or updated in the Station Locator. The turnaround time for updates will depend on the completeness of the information provided, as well as the responsiveness of the station or point of contact.
NRCan regularly compares its station data with those of other relevant trade organizations and websites. Differences in methodologies, data confirmation, and inclusion criteria may result in slight variations between NRCan's database and those maintained by other organizations. NRCan also collaborates with alternative fuel industry groups to identify discrepancies in data and develop data sharing processes and best practices. NRCan and its data collection subcontractor are currently collaborating with alternative fuel industry groups to ensure best practices are being followed for identifying new stations and confirming station changes in the most-timely manner possible.
Station Update Schedule
Existing stations in the database are contacted at least once a year on an established schedule to verify they are still operational and providing the fuel specified. Based on an established data collection schedule, the database is updated on an ongoing basis. Stations that are no longer operational or no longer provide alternative fuel are removed from the database as they are identified.
Beginning in 2021, public, non-networked electric vehicle (EV) charging stations will be proactively verified every other year, with half of the EV charging stations verified each year. This adjustment is to accommodate the growing number of EV charging stations in the Station Locator. NRCan will continue to make updates to any station record if changes are reported.
Mapping and Counting Methods
Each point on the map is counted as one station in the station count. A station appears as one point on the map, regardless of the number of fuel dispensers or electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE) ports at that location. Station addresses are geocoded and mapped using an automatic geocoding application. The geocoding application returns the most accurate location based on the provided address. Station locations may also be provided by external sources (e.g., station operators) and/or verified in a geographic information system (GIS) tool. This information is considered highly accurate, and these coordinates override any information generated using the geocoding application.
Notes about Specific Station Types
- Private Stations
The Station Locator defaults to searching only for public stations. To include private stations in the search, use the Station button on the "Advanced Filters" tab.
Stations with an access listing of "Private - Fleet customers only" may allow other entities to fuel through a business-to-business arrangement. For more information, fleet customers should refer to the information listed in the details section for that station and contact the station directly.
The Station Locator includes information on private fleet fueling stations (e.g., transit bus fueling facilities, other medium- and heavy-duty fueling and charging infrastructure) and workplace charging stations. Note that information on these stations is not always published online or in the data download but may be tracked only in the backend Station Locator database. Information tracked only in the backend database may be provided by request to the webmaster listed in the "More Information" section below.
NRCan collects and publishes data on planned station locations, particularly those that are sited and have begun the installation process. In addition, the Station Locator includes stations that are temporarily out of service or offline with plans to open again in the future. To include planned and temporarily unavailable stations in the search results, use the "Advanced Filters" tab.
The Station Locator only includes stations offering biodiesel blends of 20% (B20) and above for a certain period of time during the year. The available blends at each station location are displayed when the station location is selected.
Each point on the map is counted as one station in the station count. The number of EVSE ports and types of connectors available at each station location are displayed in the details page for each station location. Users may search by charger types, connectors, and networks using the Fuel button on the "Advanced Filters" tab.
NRCan is in the process of transitioning EV charging station counting logic to align with the hierarchy defined in the Open Charge Point Interface (OCPI) protocol: station location, EVSE port, and connector. With this transition, NRCan is updating the number of EVSE ports (formerly called charging outlets) in the Stations Locator, which represents the number of vehicles that can charge simultaneously at a station location. The Station Locator also identifies the available connector types. Both the total number of station locations and EVSE ports appear in the EV charging search results on the "Advanced Filters" tab.
The Station Locator imports ChargePoint, Circuit électrique, FLO, Greenlots, and SemaConnect network station data directly from these networks on a daily basis. Please note there may be variations in the formatting of API stations from other alternative fuels in the Station Locator. Also note, NRCan cannot edit station information for the networks listed above. To suggest edits to these stations, please contact the charging network directly with the recommended changes. For network contact information, please contact the webmaster listed in the "More Information" section below.
As the above networks transition to the OCPI protocol, NRCan works with each to integrate their OCPI-based API. This transition may result in increases to station counts because of the way that station data are shared under the protocol; one station may be split out into several new stations to represent different physical locations of EV chargers at one address (e.g., opposite sides of one parking lot). While the new stations may share the same street address, they may have different coordinates.
Please Note: Residential EV charging locations and "wall outlets" not designated for vehicle charging are not included in the Station Locator, but workplace charging locations are.
The Station Locator includes stations offering high-level ethanol-gasoline blends (E85). Users may limit their search to E85 stations offering mid-level blends, such as E30, by using the Fuel button on the "Advanced Filters" tab.
Many public propane stations serve customers other than drivers and fleets. To represent the differences, each public propane station is designated as a "primary" or "secondary" service type, with both types able to fuel propane vehicles. However, locations with a "primary" designation offer vehicle-specific fueling capabilities.
Public locations with the "primary" designation must be staffed during regular business hours and must not require drivers to call ahead in order to fuel. Primary stations must also accept credit cards or fleet cards as a payment type. To be considered "primary," the station must be able to fuel vehicles at a rate of 30-45 litres (8-12 gallons) per minute or faster, or at a rate similar to filling a gasoline vehicle.
Service designations are available in the details page for each public station. The Station Locator defaults to showing only public "primary" stations. Users may expand their search to include all propane stations by using the "Include stations with limited vehicle fueling" checkbox after choosing propane as a fuel or select this same option in the "Advanced Filters" tab.
Some compressed and liquefied natural gas stations are not able to fuel larger vehicles due to access limitations, such as a low canopy, insufficient parking adjacent to the pump, or limited space to maneuver. Natural gas station details include vehicle accessibility information, specifically the vehicle classes that can physically access the fueling infrastructure. Please note, this field does not take into account station capacity, throughput, or other considerations. Options include:
- Accommodates passenger vehicles only (Class 1-2).
- Accommodates medium-duty vehicles (Class 3-5).
- Accommodates heavy-duty vehicles (Class 6-8).
- Accommodates all vehicle sizes and classes.
Compressed natural gas stations also list fill type and fill pressure in the details page. These fields are also searchable using the Fuel button on the "Advanced Filters" tab.
Fuel cell electric vehicle drivers may have access to hydrogen stations in certain areas of the country. Because this technology is in the early commercialization stages, the status of hydrogen fueling stations may change more frequently than other fuel types. To allow users to monitor station status more closely, hydrogen stations now indicate whether or not they have reduced fueling capacity.
The Station Locator data differentiates between public hydrogen stations that are only available to a certain subset of customers (e.g., require an access card, PIN, or training) and those that are considered retail locations (e.g., accept payment at the point of sale). Access designations are available in the details page for each public station. The Station Locator defaults to showing only public retail stations. Users may expand their search to include all public hydrogen stations by selecting the "Include non-retail stations" checkbox.
Download Data
You can download the station data using:
More Information
For more information about the data, contact the webmaster.
Caution: NRCan recommends users verify a station is open, available to the public, and has the desired alternative fuel prior to making a trip to that location.
Close
Charging Infrastructure Terminology
The Alternative Fueling Station Locator uses the following charging infrastructure definitions:
- Station Location: A station location is a site with one or more EVSE ports at the same address. Examples include a parking garage or a mall parking lot.
- EVSE Port: An EVSE port provides power to charge only one vehicle at a time even though it may have multiple connectors. The unit that houses EVSE ports is sometimes called a charging post, which can have one or more EVSE ports.
- Connector: A connector is what is plugged into a vehicle to charge it. Multiple connectors and connector types (such as CHAdeMO and CCS) can be available on one EVSE port, but only one vehicle will charge at a time. Connectors are sometimes called plugs.
Location Fuel Charger Types Level 2, DC Fast All Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 DC Fast Connectors All All J1772 CCS CHAdeMO Tesla Map a Route Start location End location Fuel Distance from the Route to Show Stations Show stations within of the route Charger Types Level 2, DC Fast All Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 DC Fast Connectors All All J1772 CCS CHAdeMO Tesla Find Stations Close Level 1
Level 1 charging is a 120V standard wall plug using a J1772 connector. Provides 2 to 5 miles of range per 1 hour of charging.
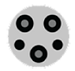 J1772
J1772
Level 2
Level 2 charging uses 240V/208V for residential or commercial charging using a J1772 connector. Provides 10 to 20 miles of range per 1 hour of charging.
 J1772
J1772
DC Fast
There are three types of DC fast charging systems depending on the type of charge port on the vehicle. Provides 60 to 80 miles of range per 20 minutes of charging.
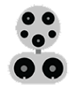 SAE CCS
SAE CCS 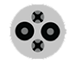 CHAdeMO
CHAdeMO  Tesla © MapTiler © OpenStreetMap contributors
Tesla © MapTiler © OpenStreetMap contributors
Edit Filters
181 station locations
525 EVSE ports
Filters chosen:
- Arkansas
- Electric
- Types: DC Fast, Level 2
- Access: Public
Use this tool to view alternative fuel corridors designated by the Federal Highway Administration and to measure the distance between stations that meet the criteria for corridors.
Explore more resources for corridors. Have a comment or concern with this tool? Please contact us.
States Fuel 50 miles between stations allowed Station Locations Designated Alternative Fuel Corridors
- iPhone App for U.S. stations
- Android App for U.S. stations
- Developer APIs
- Embed Tool
- Submit New Station
- About the Data
Source: Alternative Fuels Data Center
Please enable JavaScript to view the alternative fueling station locator.
The rebate account’s balance, comprising a portion of the $14.6 million in settlement funds the state received from the Volkswagen emissions scandal, sat Tuesday at $227,791. In the first round of rebates this year, the program reimbursed more than $200,000 in EV charging station costs.
The next round wasn’t planned to become available until 2023, but the heightened interest prompted the state energy department to open it earlier, Keogh said. She said the department is also committed to offering another round of similar rebates in 2023 through another pot of available federal funds.
The rebates are available for up to 10 Level 2 charging stations per applicant installed after Feb. 1 and available for public use. Smaller rebates are also available for places like apartment complexes and employers that make the stations accessible to employees and tenants but not the general public.
The rebates cover up to 90% of the charging station costs on government-owned property and 70% of costs for public chargers on non-government property.
For workplace or multi-unit dwelling stations, the rebates will cover up to 50%.
Full eligibility criteria and rebate application information can be found here.
Since starting the program in 2021, the rebates have covered 137 charging stations and $629,316 in costs.
Other incentives
The rebate is one of three main state incentive programs aimed at increasing the number of EV charging stations in the state.
The second state incentive is a financial assistance program that will provide up to 75% of project costs for the installation of 150-kilowatt DC fast chargers, which can charge vehicles in less than an hour.
The third is the National Electric Vehicle Infrastructure Formula Program created by the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law enacted by Congress last year. Arkansas will receive $54.1 million under the program.
NEVI
To start, the NEVI funds will be focused on the charging stations along interstates and alternative fuel corridors until those routes are “fully-built out,” meaning publicly accessible DC Fast Charging Stations every 50 miles within 1travel mile of the interchanges.
Then, focus will expand out to other routes based on need, like major state highways.
The Federal Highway Administration approved Arkansas’ NEVI plan Sept. 14. The plan includes a public survey and prioritization map that shows the EV charging gaps in the state.
Ellen Coulter, a spokeswoman for the state Department of Transportation, said the agency is developing the application process and contracts for NEVI funds. However, it must wait to implement the program until the U.S. Transportation Department finalizes its rules, expected by summer 2023.
“Our deployment strategy is to spur local market investments through a competitive procurement program to award NEVI funds to owner-operators,” Coulter said. “Owner-operators may include private sites/partners, public sites/partners, or public-private partnerships. ARDOT will not own, operate, or site EV charging stations on its own property.”
EV growth
Fortune Business Insights projects the EV market in the U.S. will continue to grow from $28.24 billion in 2021 to $137.43 billion in 2028 at a compound annual growth rate of 25.4%.
For now, Keough said state government isn’t dictating to any community whether it should be building EV charging infrastructure, but the rebate program is designed to make it easier for those entities that want to build charging stations.
In the future, she said there may be opportunities for the state to step in to fill gaps in the charging network if there is a compelling “statewide interest” in closing those gaps.
“Anyone in Arkansas who wants access to drive electric vehicles should have no worries about the accessibility of charging their vehicle, no matter where they live within the state,” Gov. Asa Hutchinson said in a statement. “This continued push for expanding the reach of Electric Vehicle infrastructure will make sure Arkansas is fully equipped for innovative technologies.”
The Arkansas Advocate is a nonprofit, nonpartisan news organization dedicated to tough, fair daily reporting and investigative journalism that holds public officials accountable and focuses on the relationship between the lives of Arkansans and public policy. This service is free to readers and other news outlets.